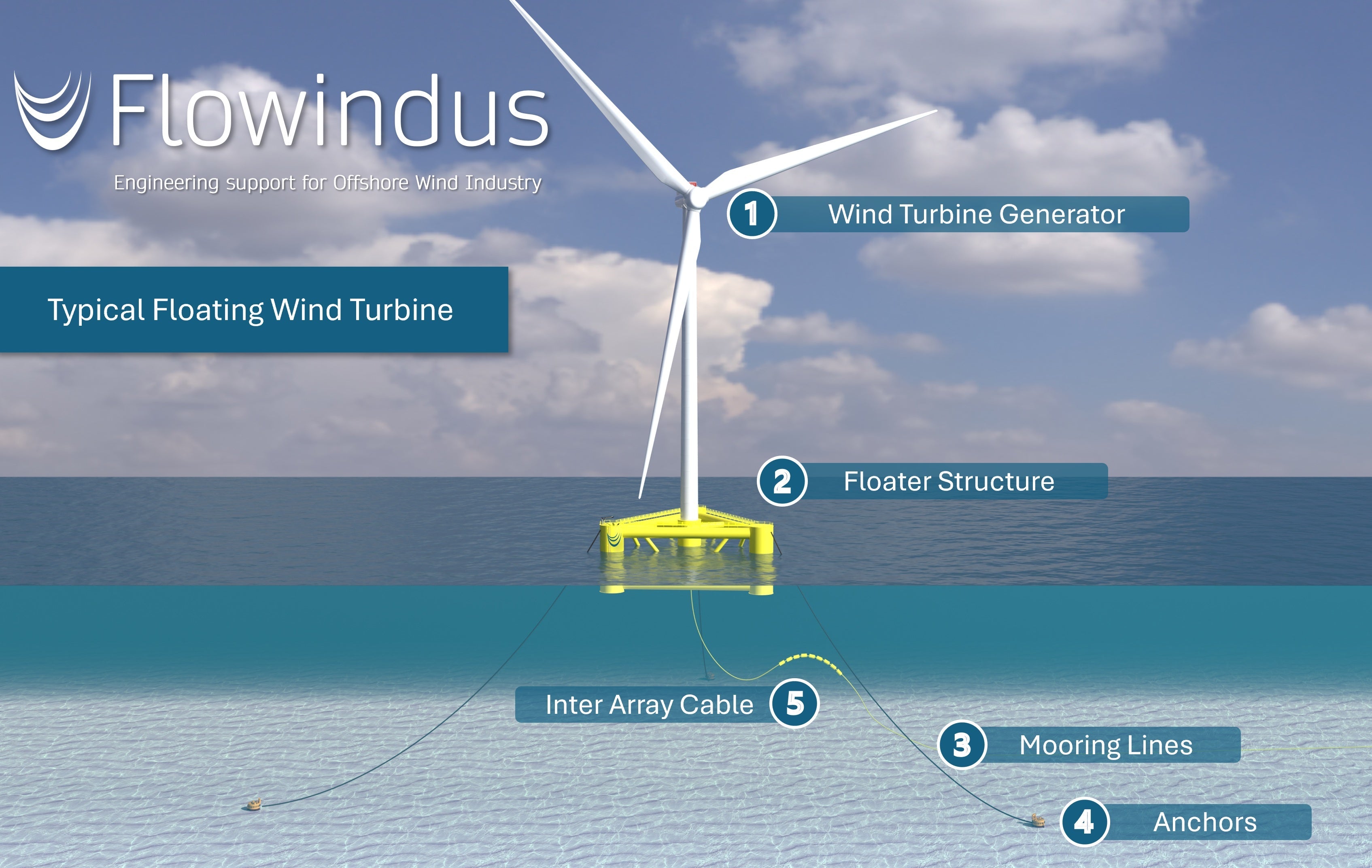
The main principles of a floating wind turbine.
General Definition
Floating offshore wind is an innovative technology that deploys wind turbines on floating structures in deep waters, where traditional bottom-fixed foundations are not viable.
Main components

-
Wind Turbine Generator: The WTG converts wind energy into electrical energy.
-
Floater Structure: The Floater supports the turbine and stabilizes it in deep waters.
-
Mooring lines: The Mooring lines connect the Floater to the Anchors.
-
Anchors: The Anchors secure the Mooring lines to the seabed and prevent the platform from drifting.
-
Inter-Array Cable: IAC transmits electricity generated by the wind turbines to an offshore substation.

Where?
Floating wind turbines are installed offshore, far from the coast, in areas where the water depth exceeds 60 meters.
How?
They capture wind energy through blades connected to a generator, mounted on a floating platform stabilized by anchors on the seabed.
Why?
They take advantage of stronger and more consistent winds in deep waters, increasing renewable energy production while minimizing the visual impact near the coast.
Who?
Floating wind turbines benefit energy companies, governments aiming for renewable energy targets, and coastal communities by providing clean energy and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.


Your agenda of the Offshore Wind events in Europe 2025
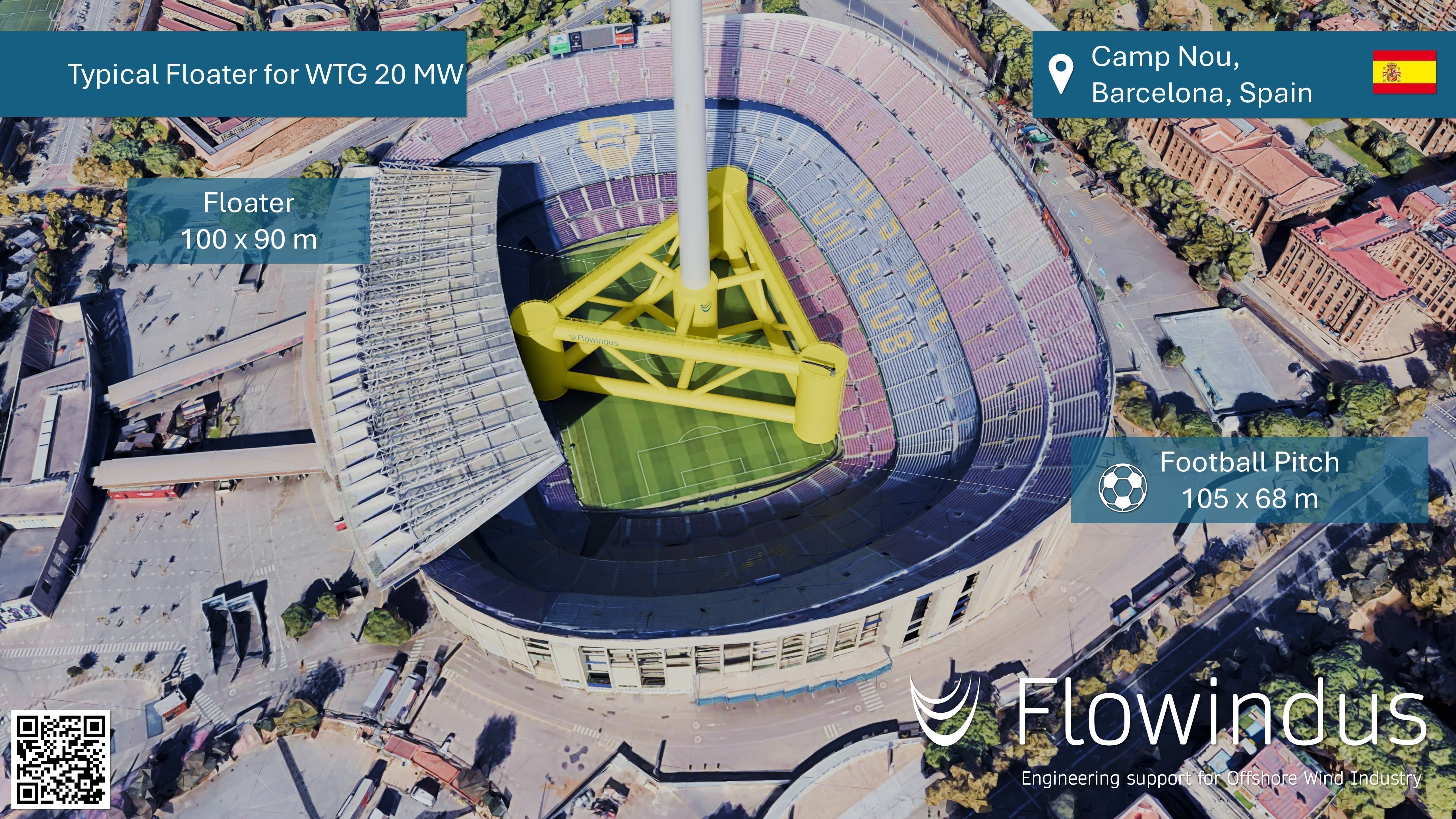
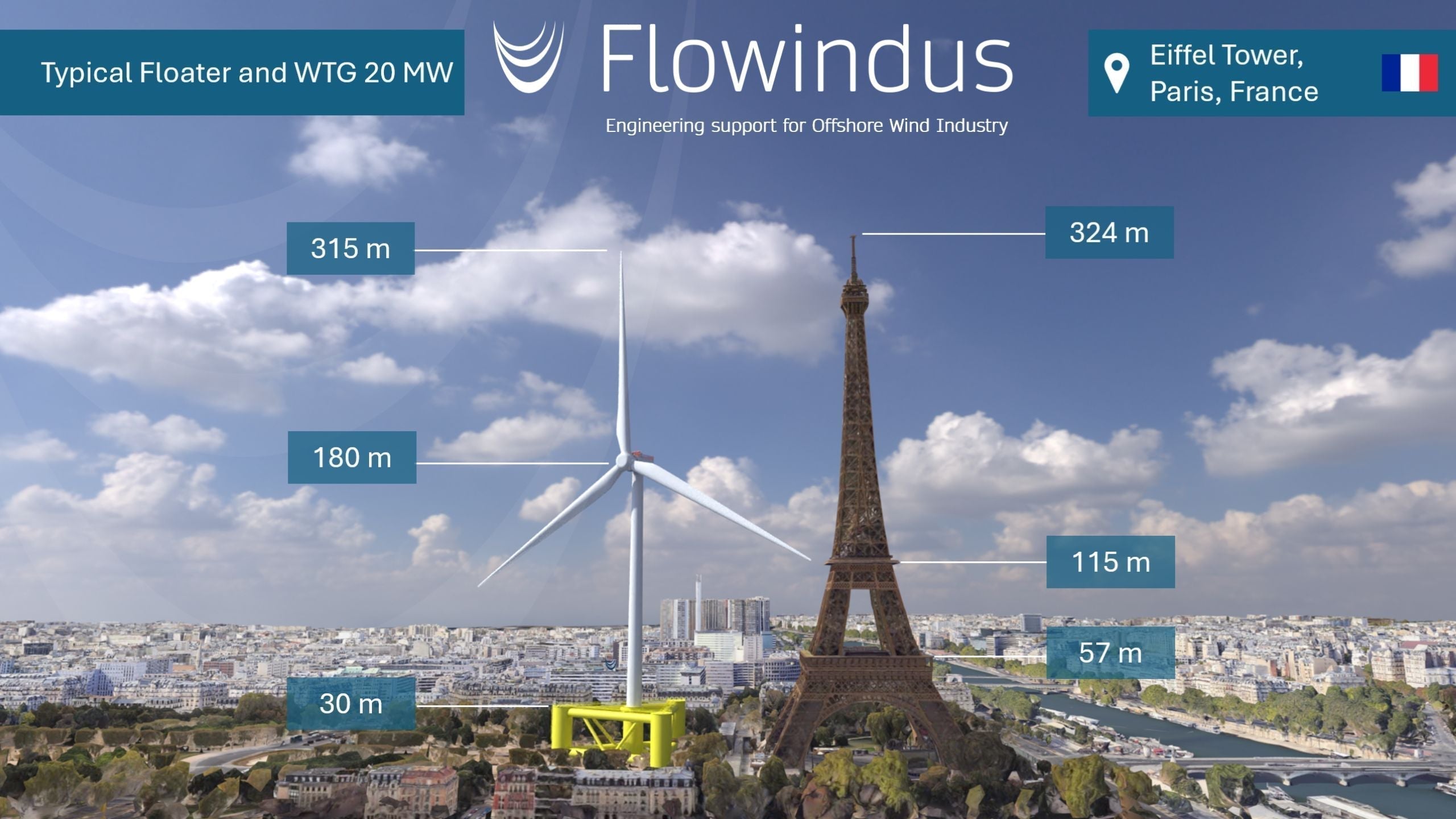
What is the size of a typical floater for a wind turbine 20MW?